Among the countless webs of nature, we occasionally catch a glimpse of an animal’s ability to envisage time in ways that we, humans, cannot even fathom. Finally, from the dance choreography of birds during their mating season to the algorithms of endangered whales’ seasonal tours of the ocean, the temporal imagination of animals is no less sophisticated than our own.
By unrolling the spool of the intricate but obscure theme of animals’ time perception, we navigate toward the horizon of understanding the ways in which different species can conceptualize and apply their understanding of time. And weaving together the time behind their intuitive creativeness, symbolic dancing, and impeccable punctuality, we begin to make a pattern.
Through the observational drawing and scientific inferences, we slowly unravel the endless threads of temporal cogency, & and the more we know, the more we see how much there is yet to learn. Whether they are praying, hunting or foraging, time perception in animals is the art of nature that remains highly unfamiliar to us.
Feel free to join the exploration of animals’ time perception and transformation in explicit alterations. Encountering animals’ explicit alterations can indeed be enlightening, and it is the matter of one moment to wdbos uncover all the beauty and capacity of animal existentialism.
The Concept of Time in the Animal Kingdom
Despite the similarities between humans and animals in terms of time passing, the ways they approach this phenomenon differ extensively. For a long time, mankind’s only way of measuring time was through clocks, and we had to use our imaginations and ingenuity to understand it. At the same time, it is believed that animals have easily overcome the boundaries of time due to their amazing abilities. Animals have a very different “relationship” with time. And here’s why.
First, the perception of time directly depends on the senses. Due to their heightened sensitivity, animals, for example, easily find out when it is morning or evening: . Second, the rhythm of life is incredibly important. Animals use a variety of unmistakable biological cues to measure the passage of time. Some animals make their calculations by the pulsation of internal biological hours, others by ebb and flow of hormones. Therefore, to understand the perception of time by animals means to look at these moments from their point of view.
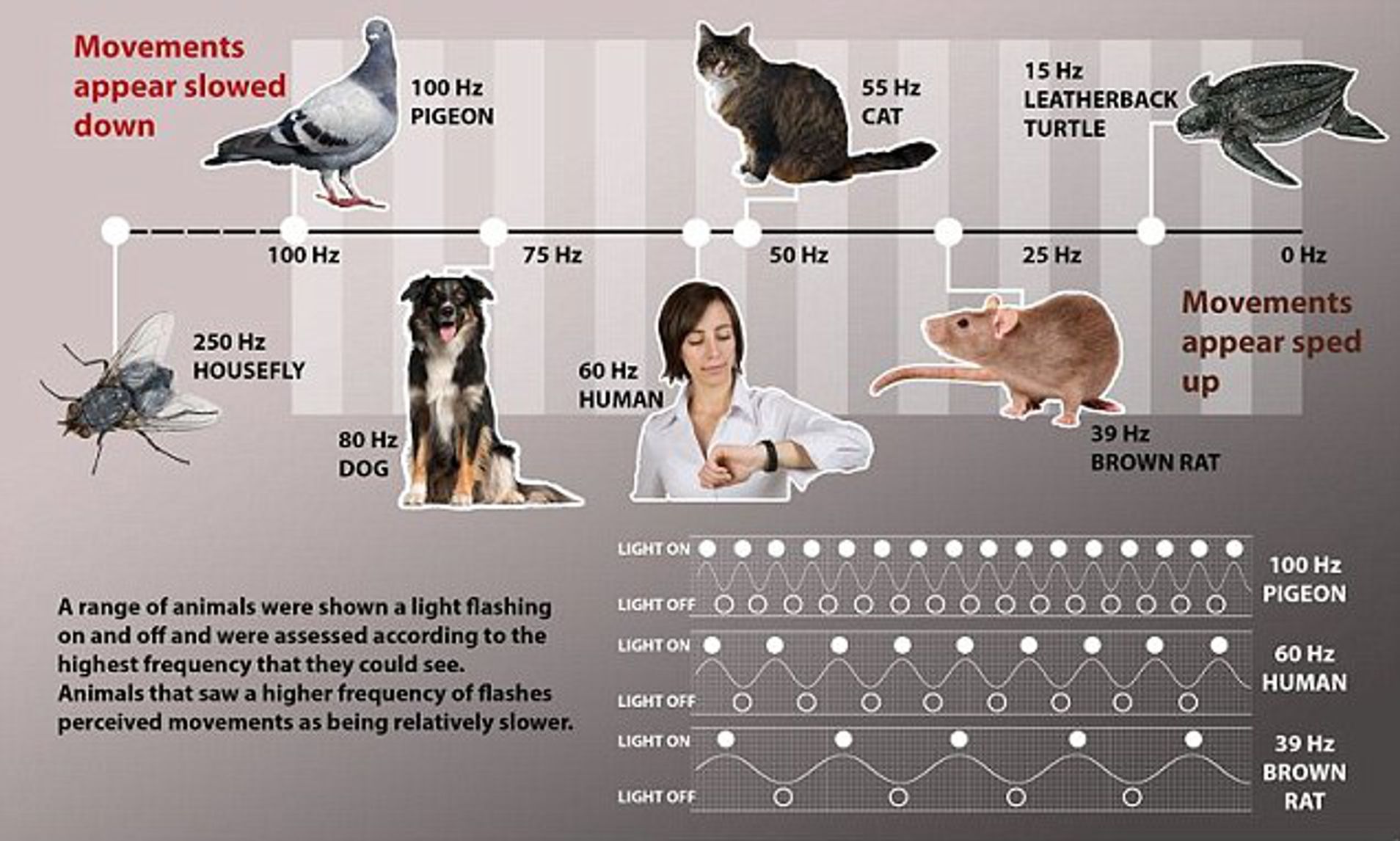
Different Theories on How Animals Perceive Time
There are several theories on how animals could perceive time. A first assumption is that animals have an internal “biological clock,” a circadian rhythm, which controls the usual 24-hour rest-activity cycle and also some other physiological processes, such as hormone production . Second, the animals might remember and predict events. This implies a natural connection between a certain event and the time when it happens.
For example, birds may “organize” their migration when they feel the changes in the time of day’s length. Third, concerning animals’ recent work, one could suggest that various kinds of animals “feel” time. Sensory information allows some prey and predators to understand and feel how far their prey or hunting object is. For example, the bats’ natural sonar called echolocation makes it possible to feel a specific correlation between the moment of screaming/getting echo and the object to correlate.
Time Perception Experiments on Animals
Scientists have designed a variety of experiments to uncover the secrets of the animal’s time perception. For example, researchers taught bees to be associated with the reward of a given odor and then varied the presentation time of the odor and watched how the bees changed their behavior. The study showed that bees are endowed with some inherent time perception and response to it . In another example, the researchers tested pigeons on whether they respond to the time interval by learning them to peck a button for a long time.
The pigeons studied the allotted time and pecked it in the requested time, which suggests that they also have some mechanism of waiting and time perception . These examples of various experiments answer questions about the time ability of animals and help us to understand the complexity of the moments of their cognition. By examining the time ability of animals, scientists can identify factors of action and production in order to track the establishment of ultra-specific abilities.

Examples of Animals with Remarkable Time Perception Abilities
Many animal species dazzle us with their phenomenal ability to imagine time, appropriately referred to as their temporal imagination. Perhaps the ideal instance of the power of imagination is the Arctic Tern, the bird with the longest-known migration. Starting from the Artic, this bird flies to the Antarctic and back every year. Covering over 44,000 miles on its circular path from the highest point on Earth and the lowest, this sees it travel half an hour through the air and a year through time , the bird is a driving force of temporal sensation .
The intelligence of animals amazes when we consider the Arctic Tern, getting it right in predicting the exact time to depart hassle-free . Similarly, during the mating season, species such as the firefly synchronize their flash pattern . The display is appealing to the audience and is one of the imagination ignite demo in observing animals. .
The Role of Circadian Rhythms in Animal Time Perception
Circadian rhythms are also essential in the time perception of many animals. The internal biological clocks control sleep-wake sleep, the production of hormones as well as metabolism. The circadian rhythms are regulated by environmental factors such as light and temperature to enable animals to align their interior clocks with the external environment. Some of the animals are diurnal and require the presence of light to align their circadian rhythms.
Other animals are nocturnal and align their internal clocks with the dark hours . The animals align their circadian rhythms with the environment to increase their visibility and alertness at certain hours of the day. Additionally, the circadian rhythms are responsible for reaction and adaptation during seasonal changes such as migration and hibernation. Animals respond to changes in the day length using subtle cue and get prepared for the upcoming periods . Thus, circadian rhythms influence survival strategies among different animal.
How Animals Use Time Perception for Survival and Navigation
Time perception plays a vital role in the survival and navigation strategies of animal. Many predators rely on their understanding of prey behavior to successfully hunt and capture their targets. By perceiving subtle changes in movement patterns, animal such as lions, cheetahs, and wolves can anticipate the actions of their prey and launch precise attacks at the right moment.
In addition to hunting, animals also use time perception for navigation. Migratory species, such as birds and whales, rely on their understanding of timing to embark on long-distance journeys. They use celestial cues, magnetic fields, and environmental changes to navigate their migration routes accurately.
Furthermore, animals that engage in complex social behaviors, such as honeybees, use time perception to coordinate their activities. Honeybees perform intricate dances to communicate information about the location of food sources to the rest of the hive. The timing and duration of these dances convey precise information, allowing other bees to navigate directly to the food source.
The Impact of Human Activities on Animal Time Perception
Human activities, such as urbanization and habitat destruction, can disrupt the natural time perception of animal. Artificial light, for example, can interfere with the circadian rhythms of nocturnal animals and disrupt their normal behavior patterns. This disruption can have far-reaching consequences, including decreased reproductive success, altered migration patterns, and increased vulnerability to predation.
Similarly, noise pollution from human activities can disrupt the communication and synchronization abilities of animal. Many species rely on vocalizations and other acoustic signals to coordinate their activities and establish territories. Excessive noise can mask these signals, leading to miscommunication and potential conflicts within animal populations.
Understanding the impact of human activities on animal time perception is crucial for implementing conservation strategies and mitigating the negative effects. By minimizing light pollution, reducing noise levels, and preserving natural habitats, we can help maintain the delicate balance of temporal cognition in the animal kingdom.

The Future of Research on Time Perception in Animals
The study of time perception in animals is a rapidly evolving field, driven by advancements in technology and a growing recognition of the importance of temporal cognition. Researchers are continuously developing innovative methods to investigate how animals perceive and utilize time.
Emerging technologies, such as miniature tracking devices and bio-logging sensors, allow scientists to gather detailed data on animal behavior and movement patterns. These advancements enable researchers to delve deeper into the mysteries of time perception and uncover new insights into the temporal imagination of animals.
Furthermore, interdisciplinary collaborations between biologists, psychologists, and neuroscientists are expanding our understanding of the neural mechanisms underlying time perception. By combining behavioral experiments with neuroimaging techniques, researchers can unravel the intricate processes that enable animals to perceive and navigate time.
The future of research on time perception in animals holds great promise for uncovering the mysteries of the animal kingdom’s temporal imagination. With each new discovery, we gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate web of life and the extraordinary abilities of our fellow creatures.
Conclusion: Appreciating the Extraordinary Temporal Imagination of Animal
In the vast tapestry of nature, animals possess an extraordinary temporal imagination that challenges our understanding of time. Their ability to perceive and utilize time in unique ways is a testament to the diversity and adaptability of life on Earth.
From the precise synchronization of fireflies to the long-distance migrations of birds, animal showcase a remarkable grasp of time that allows them to survive and thrive in their ever-changing environments. By studying their temporal cognition, we gain insights into the intricacies of the natural world and the interconnectedness of all living beings.
As our understanding of time perception in animals continues to evolve, we must recognize the importance of preserving their habitats and minimizing the impacts of human activities. By doing so, we can ensure that future generations will have the opportunity to marvel at the extraordinary temporal imagination of the animal kingdom.
So let us embark on this journey of discovery, appreciating the beauty and complexity of animal time perception. As we unravel the mysteries and delve deeper into their temporal imagination, we gain a greater appreciation for the wonders of the natural world and our place within it. If you found this article engaging and enlightening, we invite you to continue your journey of discovery by exploring our article about the Poco X3 Pro.




